COMP 3511: Lecture 1
Date: 2024-09-26 13:41:44
Reviewed:
Topic / Chapter: Basic OS
summary
❓Questions
Notes
Introduction to the Course
-
Introduction
- learning goals
- fundamental principles, strategies, and algorithms
- for design & implementation of operating systems
- analyze & evaluate OS functions
- understand basic structure of OS kernel
- and identify relationship between various subsystems
- identify typical events / alerts / symptoms
- indicating potential OS problems
- design & implement programs for basic OS functions and algorithms
- fundamental principles, strategies, and algorithms
- course overview
- overview (4)
- basic OS concept (2)
- system architecture (2)
- process and thread (12)
- process and thread (4)
- CPU scheduling (4)
- synchronization and synchronization example (2)
- deadlock (2)
- memory and storage (8)
- memory management (2)
- virtual memory (3)
- secondary storage (1)
- file systems and implementation (2)
- protection (1)
- protection (1)
- security - optional
- overview (4)
- learning goals
Operating System
-
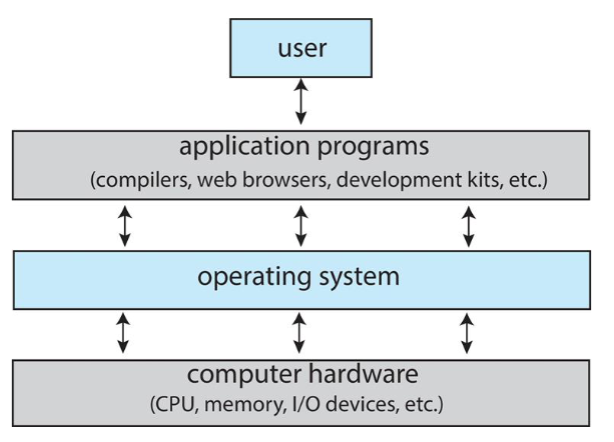
Operating system components
- users: people, machine, other computers / devices
- application programs: defining ways how system resources are used
- to solve user problems
- e.g. editors, compilers, web browsers, video games, etc.
- operating system: controls & coordinates use of computing resources
- among various application & different users
- hardware: basic computing resources: CPU, memory, IO devices
-
Operating system introduction
- OS: a (complex) program working as intermediary between: user-applications and hardware
- iOS, MS Window, Android, Linux, etc.
- OS goals:
- execute user programs & solve user problems easier
- make computer system: convenient to use
- manage & use computer hardware efficiently
- user view:
- convenience, easy of use, good performance & utility
- user: doesn't care about resource utilization & efficiency
- system view:
- OS: resource allocator & control program
- no universally accepted definition, but:
- "everything vendors ships when you order an OS"
- OS as a resource allocator
- managing both SW & HW resources
- decides among conflicting requests: for efficient & fair resource use
- OS as a control program
- controls: execution of programs, prevent errors & improper use of computer
- OS: manages & controls hardware
- helps to facilitate (user) programs to run
- OS: a (complex) program working as intermediary between: user-applications and hardware
-
OS breakdown
- kernel: one program always running on computer
- provides essential functionalities
- middleware: set of SW frameworks: provide additional services to app dev
- e.g. DB, multimedia, graphics
- popular in mobile OS
- all else:
- system programs
- application programs
- OS includes:
- always running kernel
- middleware frameworks: for easy app development & additional feature
- system programs: aid in managing system while running
- kernel: one program always running on computer
-
Operating system tasks
- depends on: PoV (user vs. system) and target devices
- shared computers (mainframe, minicomputer)
- OS: need to keep all users satisfied
- performance vs. fairness
- individual systems (e.g. workstations) with dedicate resources
- performance > fairness; may use shared resource from servers
- mobile devices: resource constrained
- target specific user interfaces (touch screen, voice detection)
- optimized for usability & battery life
- computers / computing devices w/ little-no UI
- embedded systems: present within home devices, automobiles, etc.
- run real-time OS
- design: run primarily without user intervention
- embedded systems: present within home devices, automobiles, etc.
Computer System Organization
-
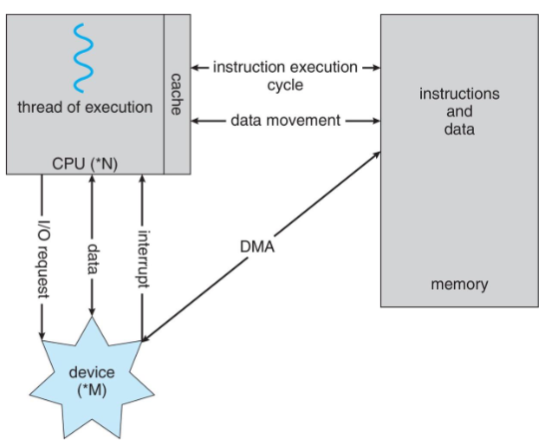
Computer system organization
- one or more CPU cores & device controllers: connected through common bus
- providing access to shared memory
- goal: concurrent execution of CPUs and devices
- compete for memory cycles w/ shared bus
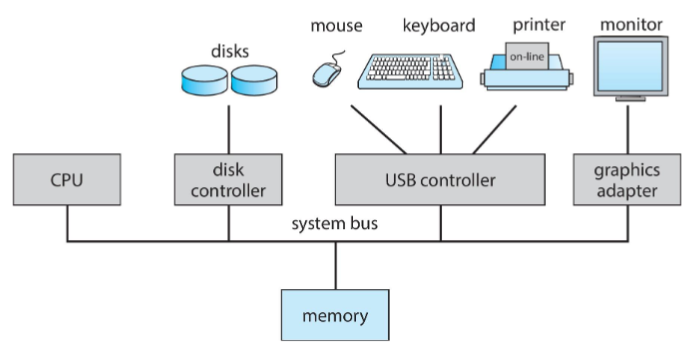
- compete for memory cycles w/ shared bus
- one or more CPU cores & device controllers: connected through common bus
-
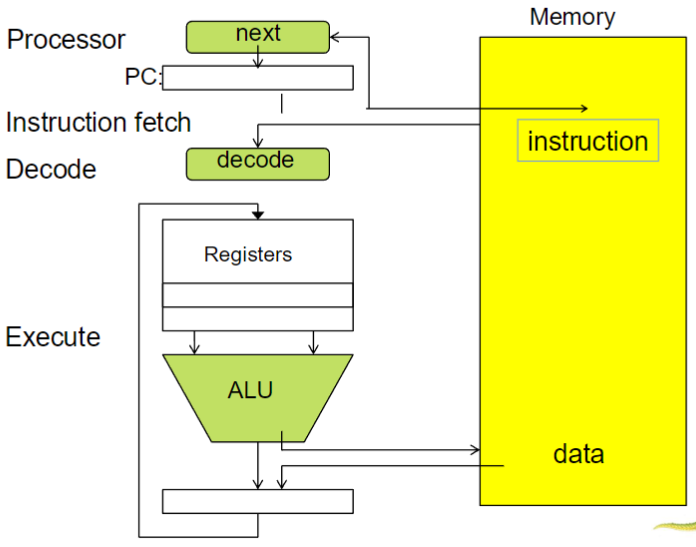
Von Neumann architecture: composition
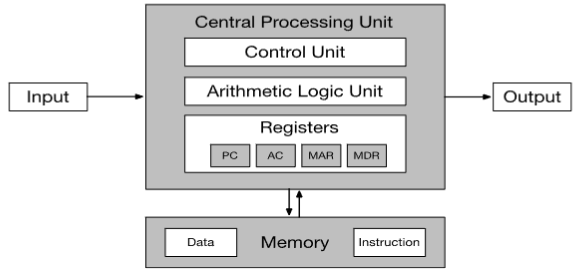
- CPU: contains ALU & processor registers
- programmer counter (PC)
- accumulator (AC)
- memory address register (MAR)
- memory data register (MDR)
- control unit: contains
- instruction register (IR)
- program counter (PC)
- memory: w/ data and instructions
- as well as caches
- external mass storage / secondary storage for more space
- input-output mechanism
- CPU: contains ALU & processor registers
-
Von Neumann architecture
- steps
- fetch instruction
- decode instruction
- fetch data
- execute instruction
- write back (if any)
diagrams
- steps